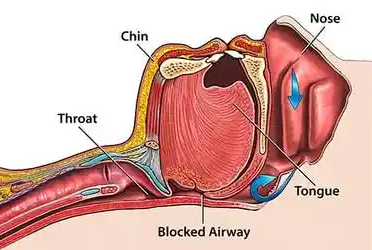
Obstructive sleep apnea refers to the obstruction in part, or all the airways during sleep, leading to reduced or absent breathing during sleep.
When you sleep, your muscles relax, including those in your throat. In some people the relaxing muscles cause the airways to narrow. This can reduce the amount of air flowing in and out of your airways. This makes you snore
It’s Called OSA Because
Obstructive: There’s an obstruction in the airway.
Sleep: It happens when you’re asleep.
Apnoea: It means you stop breathing.
If your throat closes completely, you stop breathing for a time. This is called an apnea it can last for 10 seconds or more. When the closure is partial, it is called hypopnea and it leads to partial reduction in breathing.
Symptoms of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
In OSA, your airway collapses , stopping air from travelling to and from your lungs, disturbing your sleep.
Common obstructive sleep apnea symptoms can be divided into sleeping and day symptoms, There are:
During sleep
- Night sweats
- Restlessness during sleep
- Snoring
- Waking up suddenly and feeling like you’re gasping or choking
- Hypersalivation, teeth grinding
- Trouble getting up in the mornings
- Nocturia (frequent urination at night)
- High blood pressure
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
During day time
- Waking up sleepy and unrefreshed
- Daytime sleepiness or fatigue
- Dry mouth or sore throat when you wake up
- Headaches in the morning
- Poor sex drive (libido)
- Trouble concentrating, forgetfulness, depression , or crankiness
- Excessive daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia)
- Changes in mood
If you share a bed with someone, they’ll probably notice your sleep apnea before you do.
Symptoms In Children
These may not be very clear, and may include:
- Bed-wetting
- Choking or drooling
- Sweating a lot at night
- Ribcage moves inward when they breathe out
- Learning and behavior problems
- Problems at school
- Sluggishness or sleepiness (often seen as laziness)
- Snoring
- Teeth grinding
- Restlessness in bed
- Breathing that pauses or stops
- Unusual sleeping positions, such as sleeping on their hands and knees , or with their neck bent far back
Causes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea usually happens when the muscles that control your airway relax too much, narrowing your throat. You wake up for a moment to reopen your airway, but you probably won’t remember doing it. This might happen dozens of times each hour.
Other things that block your throat can cause obstructive sleep apnea, like obesity, swollen tonsils, and health problems like endocrine disorders or heart failure.
OSA, also appears to have a genetic component; those with a family history of it are more likely to develop it themselves.
Factors That Increases The Risk of OSA.
The following factors increases the risk of OSA which includes;
Excess weight: Obesity greatly increases the risk of sleep apnea. Fat deposits around your upper airway can obstruct your breathing.
Neck Circumference: People with thicker necks might have narrower airways.
Narrowed Airway: You might have inherited a narrow throat. Tonsils or adenoids also can enlarge and block the airway, particularly in children.
Gender: Men are two to three times more likely to have sleep apnea than are women. However, women increase their risk if they’re overweight, and their risk also appears to rise after menopause.
Age: Sleep apnea occurs significantly more often in older adults.
Family History: Having family members with sleep apnea might increase your risk.
Use Of Alcohol: Sedatives or tranquilizers. These substances relax the muscles in your throat, which can worsen obstructive sleep apnea.
Smoking: Smokers are three times more likely to have obstructive sleep apnea than are people who have never smoked. Smoking can increase the amount of inflammation and fluid retention in the upper airway.
Nasal Congestion: If you have difficulty breathing through your nose, whether from an anatomical problem or allergies. You’re more likely to develop obstructive sleep apnea.
Medical conditions: Congestive heart failure, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes and Parkinson’s disease are some of the conditions that may increase the risk of obstructive sleep apnea. Polycystic ovary syndrome, hormonal disorders, prior stroke and chronic lung diseases such as asthma also can increase risk.
Also read: Daily Lifestyles to Improve Brain health and Memory
Benefits of Drinking Moderate Nescafe Coffee Everyday
Complications Of OSA
Complications of obstructive sleep apnea can include:
- Sleepiness during the day and trouble concentrating. Adults may have a higher risk of accidents, and children may have a hard time at school.
- Cardiovascular problems such as heart attack, high blood pressure, unusual heart rhythms, or stroke
- Eye problems such as glaucoma and dry eye
- Complications with medications and surgery. Obstructive sleep apnea is also a concern with certain medications and general anesthesia. People with sleep apnea might be more likely to have complications after major surgery because they’re prone to breathing problems, especially when sedated and lying on their backs.
Treatment for OSA
Lifestyle changes
For milder cases of obstructive sleep apnea, your doctor might recommend lifestyle changes:
- Lose weight if you’re overweight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Drink alcohol moderately, if at all. Don’t drink in the hours before bedtime.
- Quit smoking.
- Use a nasal decongestant or allergy medications.
- Don’t sleep on your back.
- Avoid taking sedative medications such as anti-anxiety drugs or sleeping pills.
If these measures don’t improve your sleep or if your apnea is moderate to severe, then your doctor may recommend other treatments. Certain devices can help open up a blocked airway. In other cases, surgery may be necessary.
Before you have surgery, tell your doctor about your sleep apnea and how it’s being treated.
Related Posts: Good Sleeping Habits That Everyone Need
6 Healthy Benefits Of Exercise To The Heart






Leave a Reply